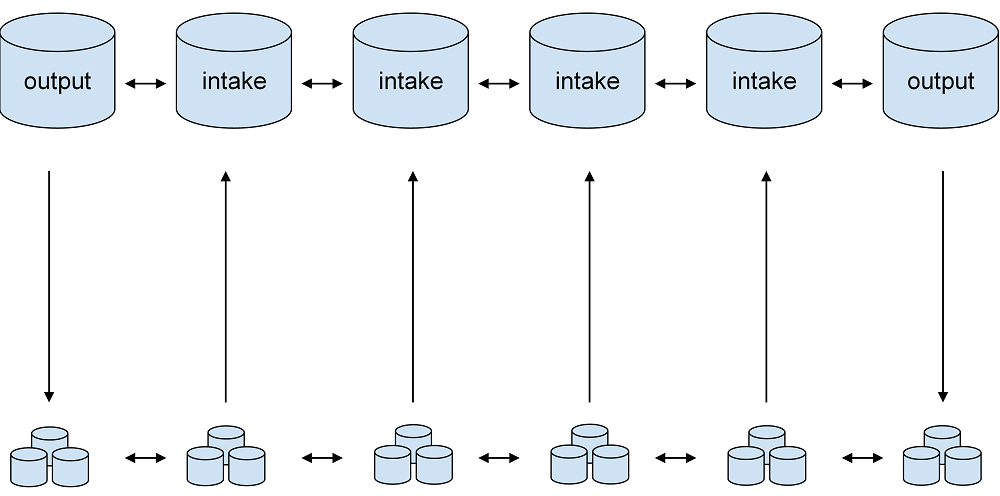
full node cluster valve configuration
overview
the current data sync logic depends on a node asking another node for what it needs (fast but incomplete), instead of asking what there is (slow but complete). as a result, the concept of a full node is unlikely or coincidental. as a result transaction data will be missing.
objective
using nothing but configuration settings, create and operate a cluster valve of full nodes that aspire to make outbound connections to collect all transaction data for a given shard and accept inbound connections to make the data available to all standard nodes.
full nodes insert and store transaction data and excuse themselves from data processing using a combination of the following configurations:
output node
connection inbound: many (accept many subscribers requesting data)
connection outbound: few (only make outbound connections to intake node ip addresses within the valve cluster)
preferred nodes: small number of intake node ip addresses
pruning: off
audit round: off
validation round: off
sync plan inbound: "what do you need"
sync plan outbound: none
peer rotation frequency: passive
private key: none
intake node
connection inbound: few (only accepting the number output node ip addresses within the valve cluster)
connection outbound: many (fetching data from as many standard nodes as possible)
preferred nodes: small number of output node ip addresses
pruning: off
audit round: off
validation round: off
sync plan inbound: none
sync plan outbound: "what do you have?" instead of "here is what I need"
peer rotation frequency: fast, constant, active
private key: none
hardware
low cpu, low ram, large disk, fast network
task exclusion
do not validate, audit or prune data. do not listen for key_identifier.
database exclusion
in consideration of the task exclusions, indexes may be removed and tables may go unpopulated.
full nodes in a cluster valve